Fiber to the home (FTTH) is the delivery of a communications signal over optical fiber from the operator’s switching equipment all the way to a home or business, thereby replacing existing copper infrastructure such as telephone wires and coaxial cable. Fiber to the home is a relatively new and fast growing method of providing vastly higher bandwidth to consumers and businesses, and thereby enabling more robust video, internet and voice services.
1. Greater capacity
Typically copper is limited to gigabit speed whereas fiber will handle at least 10 gigabit. This is becoming more of an issue as cloud computing demands shorter network response times.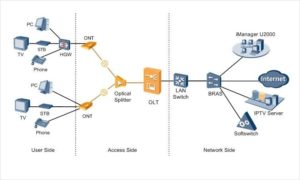
2. Less signal degradation
Fiber can cover much greater distances without significant signal loss. This results in higher speed and dependability, and also reduces the amount of power needed to transmit data.
3. Stronger and more reliable
Fiber has a strength more than four times that of copper. Copper is very malleable and is susceptible to signal degradation due to being stretched, twisted or kinked. It requires  insulation and shielding which are both vulnerable to damage. The FTTH broadband connection will spark the creation of products not yet dreamed of as they open new possibilities for data transmission rate. Using the past as a guide, think what items that now seem commonplace were not even on the drawing board five or 10 years ago.
insulation and shielding which are both vulnerable to damage. The FTTH broadband connection will spark the creation of products not yet dreamed of as they open new possibilities for data transmission rate. Using the past as a guide, think what items that now seem commonplace were not even on the drawing board five or 10 years ago.
4. Secure and resistant to electrical noise
 Fiber transmits light so it does not need shielding from electrical interference. It can be installed close to existing infrastructure such as transmission lines, cell phone repeaters or, on a smaller scale, WiFi hubs. Also, because of the use of light, it is more secure than copper as it is very difficult to tap into.
Fiber transmits light so it does not need shielding from electrical interference. It can be installed close to existing infrastructure such as transmission lines, cell phone repeaters or, on a smaller scale, WiFi hubs. Also, because of the use of light, it is more secure than copper as it is very difficult to tap into.
Fiber to the home is a relatively new and fast growing method of providing vastly higher bandwidth to consumers and businesses, and thereby enabling more robust video, internet and voice services. More technology about the fiber to the home is to be expected!
